Detection of a Topological Pair Density Wave State in UTe2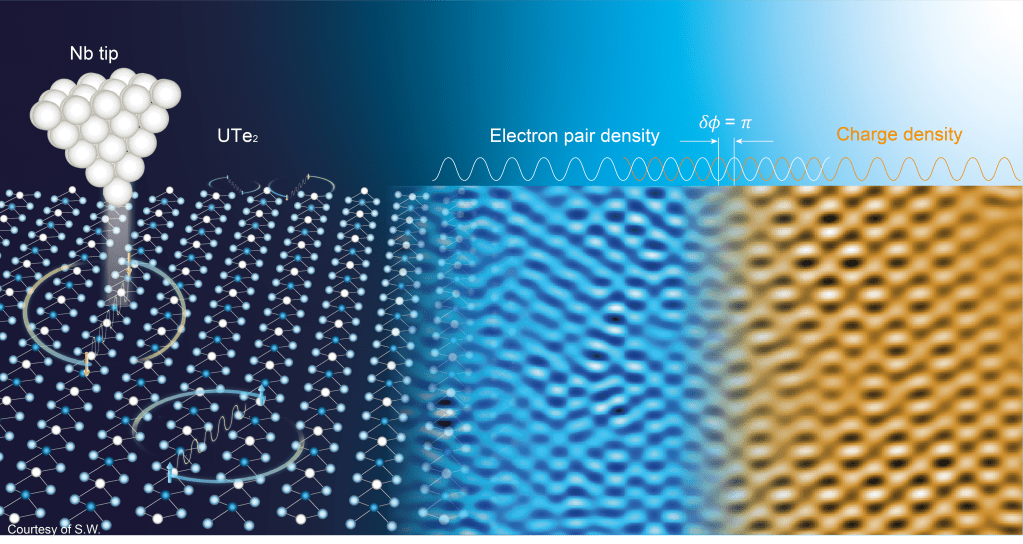
Spin-triplet topological superconductors should exhibit unprecedented electronic properties including fractionalized quantum states relevant to quantum information processing. Although UTe2 may embody bulk topological superconductivity, its superconductive order-parameter remains unknown. Many diverse forms for the order parameters are physically possible in such heavy fermion materials. Moreover,intertwined density waves of spin (SDW), charge (CDW) and pairs (PDW) may interpose, with the latter exhibiting spatially modulatingsuperconductive order-parameter, electron pair density and pairing energy-gap. Hence, the newly discovered CDW state in UTe2 motivates the prospect that a PDW state may exist in this material. To search for a PDW in UTe2, we visualize the pairing energy-gap with ueV-scale energy-resolution using superconductive STM tips. We detect three PDWs, each with peak-peak gap modulations circa 10 ueV and at incommensurate wavevectors Pi: i = 1,2,3 that are indistinguishable from the wavevectors Qi: i = 1,2,3 of the prevenient CDW. Concurrent visualization of the UTe2 superconductive PDWs and the non-superconductive CDWs reveals that every Pi:Qi pair exhibits a relative spatial phase of π. From these observations, and given UTe2 as a spin-triplet superconductor,this PDW state should be a spin-triplet pair density wave. While such states do exist in superfluid 3He, for superconductors they are unprecedented.
Nature 618, 921–927 (2023).
Press release:
Physics World: Topological superconductor harbours unusual crystalline state
Nature News & Views: Widespread pair density waves spark superconductor search
Oxford news: Breakthrough identifies unprecedented state of topological quantum matter
Scattering Interference Signature of a Pair Density Wave State in the Pseudogap Phase.
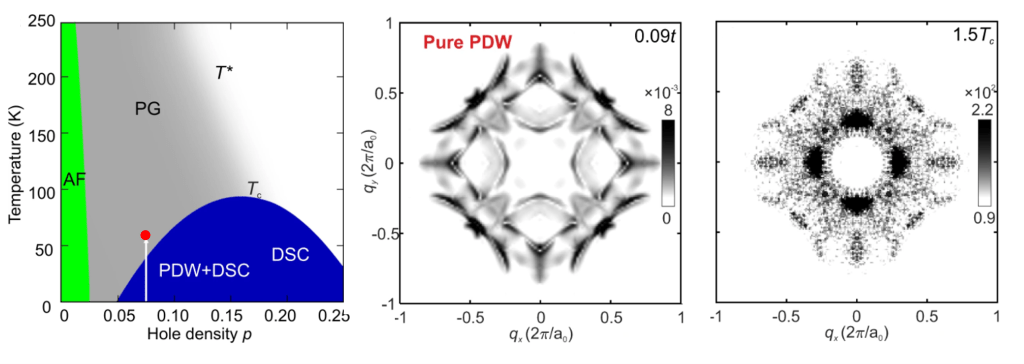
An unidentified quantum fluid designated the pseudogap (PG) phase is produced by electron-density depletion in the CuO2 antiferromagnetic insulator. Current theories suggest that the PG phase may be a pair density wave (PDW) state characterized by a spatially modulating density of electron pairs. Such a state should exhibit a periodically modulating energy gap ΔP(r) in real-space, and a characteristic quasiparticle scattering interference (QPI) signature ΛP(q) in wavevector space. By studying strongly underdoped Bi2Sr2CaDyCu2O8 at hole-density ~0.08 in the superconductive phase, we detect the 8a0-periodic ΔP(r) modulations signifying a PDW coexisting with superconductivity. Then, by visualizing the temperature dependence of this electronic structure from the superconducting into the pseudogap phase, we find the evolution of the scattering interference signature Λ(q) that is predicted specifically for the temperature dependence of an 8a0-periodic PDW. These observations are consistent with theory for the transition from a PDW state coexisting with d-wave superconductivity to a pure PDW state in the Bi2Sr2CaDyCu2O8 pseudogap phase.
Nature Communications, 12, 6087, 2021.