Discovery of Orbital Ordering in Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+x
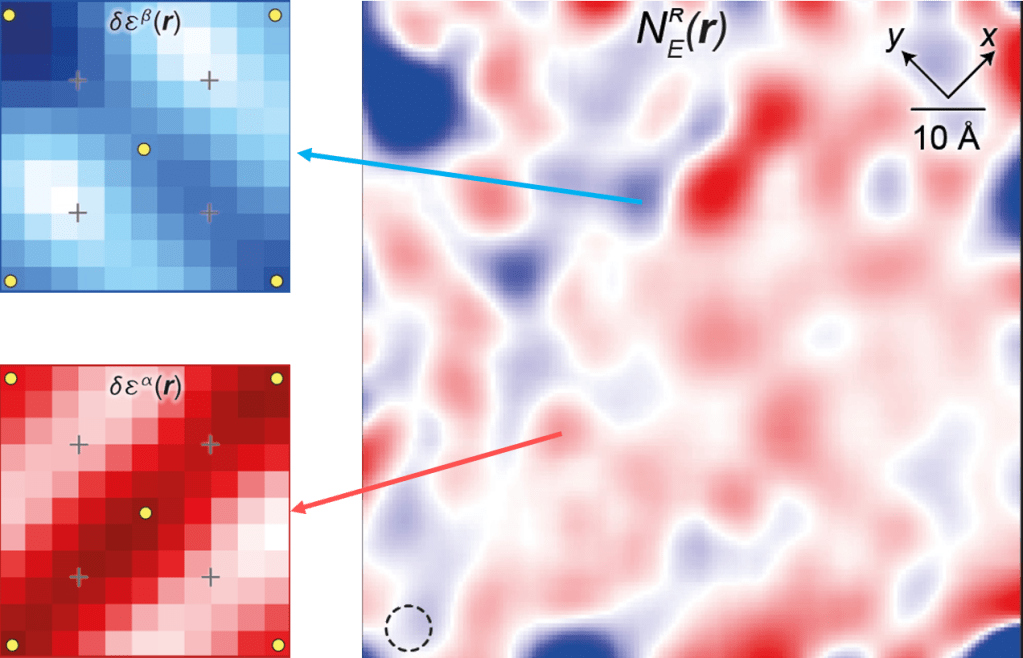
The primordial ingredient of cuprate superconductivity is the CuO2 unit cell. Here, theoretical attention usually concentrates on the intra-atom Coulombic interactions dominating the 3d9 and 3d10 configurations of each copper ion. However, if Coulombic interactions also occur between electrons of the 2p6 orbitals of each planar oxygen atom, spontaneous orbital ordering may split their energy levels. This long predicted intra-unit cell symmetry breaking should then generate an orbital ordered phase, for which the charge-transfer energy E separating the 2p6 and 3d10 orbitals is distinct for the two oxygen atoms. Here we introduce sublattice resolved ε(r) imaging techniques to CuO2 studies and discover intra-unit-cell rotational symmetry breaking of ε(r), with energy-level splitting between the two oxygen atoms on the 50 meV scale. Spatially, this state is arranged in Ising domains of orthogonally oriented orbital order that appear bounded by dopant ions, and within whose domain walls low energy electronic quadrupolar two-level systems occur. Overall, these data reveal a Q=0 orbitally ordered state that splits the energy levels of the oxygen orbitals by ~50 meV, in CuO2.
Nature Materials, 23, 492–498, 2024.
Press release: Oxford news: Long-predicted quantum state confirmed
Scattering Interference Signature of a Pair Density Wave State in the Pseudogap Phase.
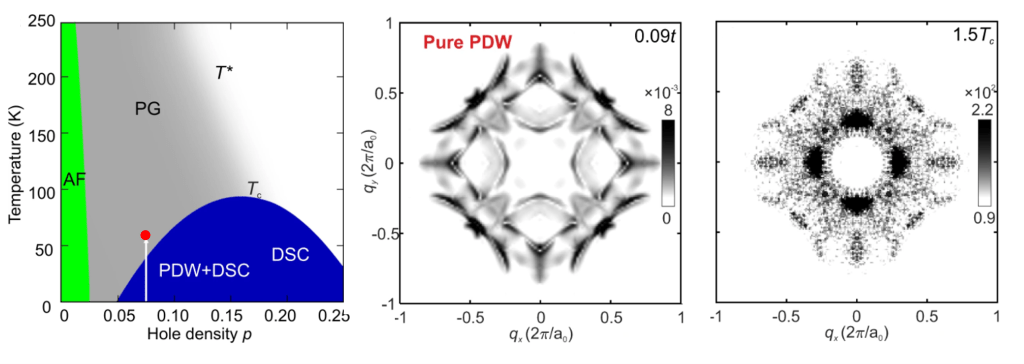
An unidentified quantum fluid designated the pseudogap (PG) phase is produced by electron-density depletion in the CuO2 antiferromagnetic insulator. Current theories suggest that the PG phase may be a pair density wave (PDW) state characterized by a spatially modulating density of electron pairs. Such a state should exhibit a periodically modulating energy gap ΔP(r) in real-space, and a characteristic quasiparticle scattering interference (QPI) signature ΛP(q) in wavevector space. By studying strongly underdoped Bi2Sr2CaDyCu2O8 at hole-density ~0.08 in the superconductive phase, we detect the 8a0-periodic ΔP(r) modulations signifying a PDW coexisting with superconductivity. Then, by visualizing the temperature dependence of this electronic structure from the superconducting into the pseudogap phase, we find the evolution of the scattering interference signature Λ(q) that is predicted specifically for the temperature dependence of an 8a0-periodic PDW. These observations are consistent with theory for the transition from a PDW state coexisting with d-wave superconductivity to a pure PDW state in the Bi2Sr2CaDyCu2O8 pseudogap phase.
Nature Communications, 12, 6087, 2021.